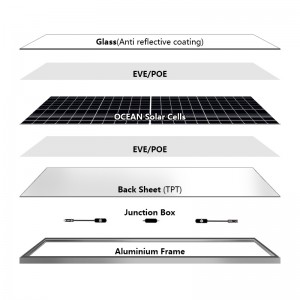
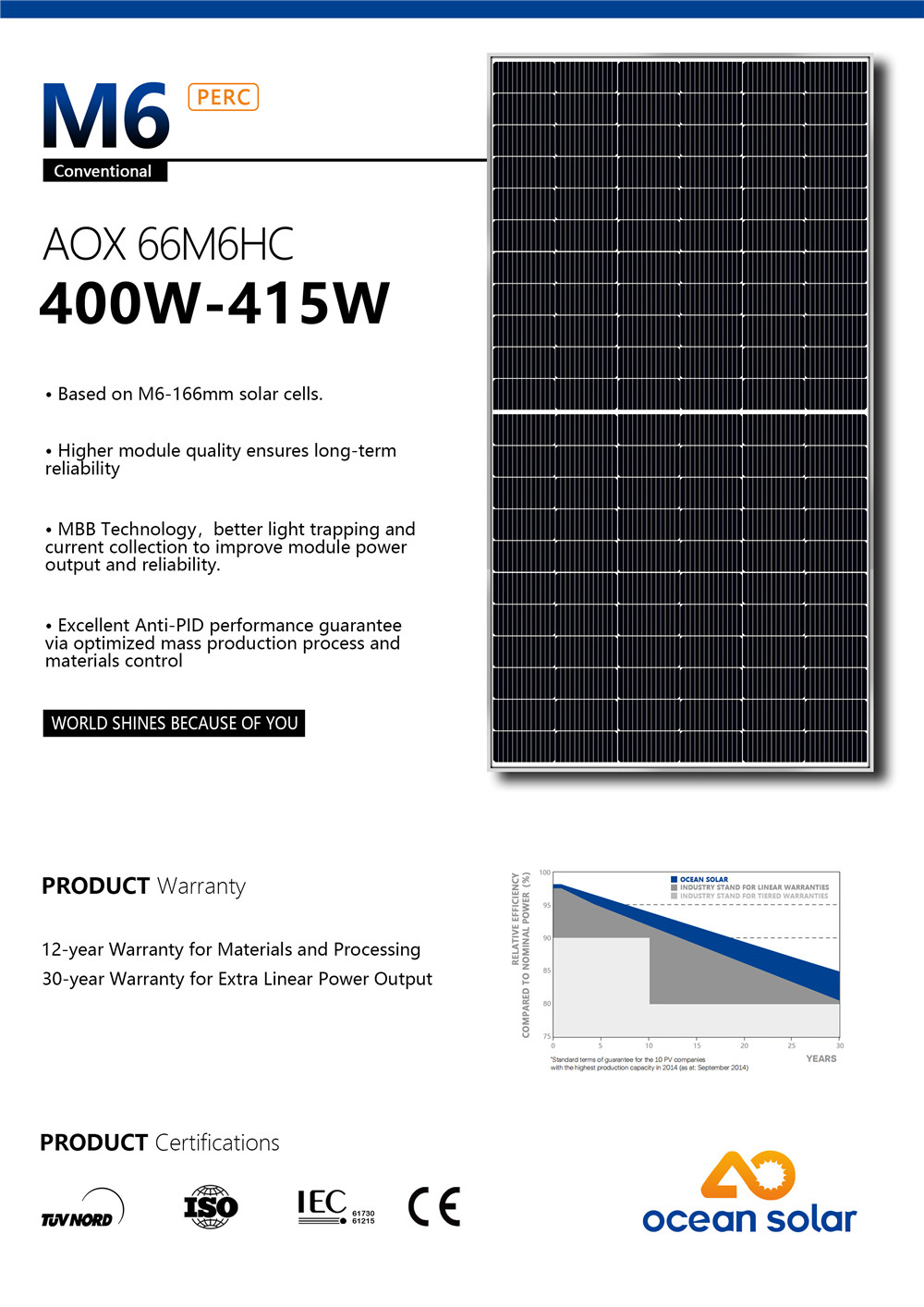
M6 MBB PERC 132 half cells 400W-415W solar module
Ultra-high Power Generation/Ultra-high Efficiency
Enhanced Reliability
Lower LID / LETID
High Compatibility
Optimized Temperature Coefficient
Lower Operating Temperature
Optimized Degradation
Outstanding Low Light Performance
Exceptional PID Resistance
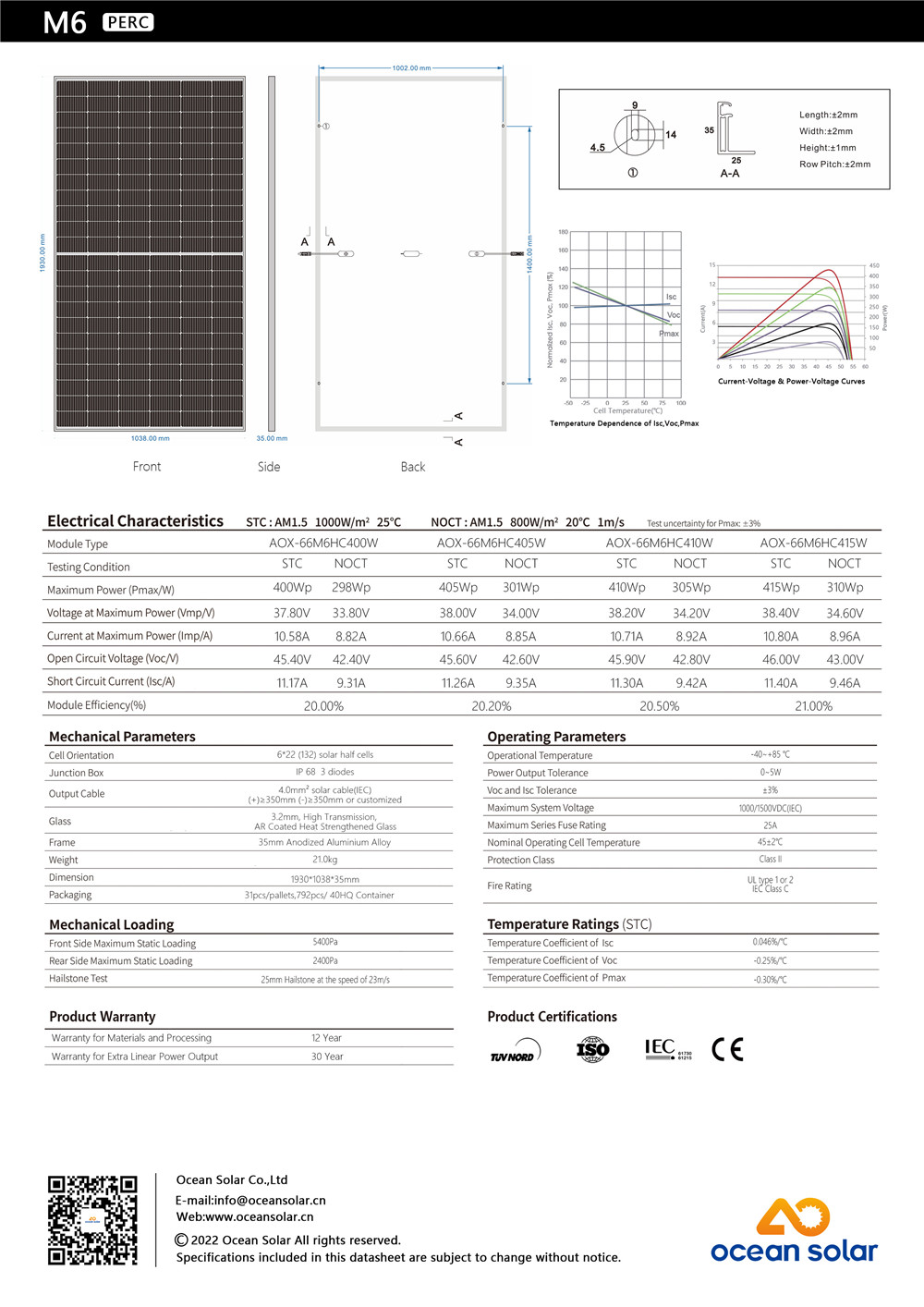
| Cell | Mono 166*83mm |
| No. of cells | 132(6×22) |
| Rated Maximum Power(Pmax) | 400W-415W |
| Maximum Efficiency | 20.0-20.7% |
| Junction Box | IP68,3 diodes |
| Maximum System Voltage | 1000V/1500V DC |
| Operating Temperature | -40℃~+85℃ |
| Connectors | MC4 |
| Dimension | 1755*1038*35mm |
| No.of one 20GP container | 336PCS |
| No.of one 40HQ container | 792PCS |
12-year warranty for materials and processing;
30-year warranty for extra linear power output.

* Advanced automated production lines and first-class brand raw material suppliers ensure that solar panels are more reliable.
* All series of solar panels have passed TUV, CE, CQC, ISO,UNI9177- Fire Class 1 quality certification.
* Advanced Half-cells, MBB and PERC solar cell technology, higher solar panel efficiency and economic benefits.
* Grade A quality, more favorable price, 30 years longer service life.
Widely used in residential PV system, commercial & industrial PV system, utility-scale PV system, solar energy storage system, solar water pump, home solar system, solar monitoring, solar street lights, etc.
MBB and PERC are two different types of solar panel technologies designed to increase the efficiency and reliability of solar panels. While both technologies aim to improve the performance of solar panels, they do so through different methods.
An MBB (multiple bus bar) solar panel is a module that uses a large number of smaller metal strips or bus bars to collect power from solar cells. The MBB design allows more electricity to be collected and transmitted from the panels to the inverter, increasing the efficiency of the solar panels. Additionally, MBB panels are more durable than traditional solar panels because the smaller busbars reduce the likelihood of cracking and damage from environmental factors.
PERC (Passivated Emitter Rear Cell) solar panels, on the other hand, use a more complex design to achieve higher efficiencies. PERC designs include adding a passivation layer to the back of the solar cell to reduce electron recombination on the back of the cell. This reduces energy loss that would otherwise reduce the efficiency of the solar panel. Additionally, PERC solar panels have a silver back layer that reflects light back into the cell, increasing the amount of energy absorbed and converted into electricity.
In terms of efficiency, PERC solar panels are the more efficient technology today, with an efficiency rating of 19-22% compared to 16-19% for MBB panels. However, MBB panels have their own set of advantages. For example, MBB panels are cheaper to manufacture than PERC panels, making them easier to install in homes. Also, while PERC panels have higher initial efficiency ratings, they tend to be more sensitive to shading and pollution, and lose efficiency more quickly over time.
When deciding which type of solar panel to choose, it's important to consider factors other than efficiency. Other things to consider include:
1. Cost: MBB panels tend to be more cost-effective than PERC panels, making them a more accessible option for homeowners and small businesses.
2. Durability: MBB panels are generally more durable than PERC panels because the smaller bus bars reduce the possibility of damage from environmental factors.
3. Shading: PERC panels are more sensitive to shading than MBB panels and may lose efficiency faster over time if shading is an issue in your area.
4. Government Initiatives: In some regions, there may be government initiatives that favor one technology over another. It's important to research the policies in your area to see which type of panels will be most beneficial.
Overall, both MBB and PERC solar panel technologies have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. The best choice for your home or business depends on a variety of factors, including efficiency, cost, durability, and environmental considerations.